212x Filetype PDF File size 0.56 MB Source: d2cyt36b7wnvt9.cloudfront.net
Class- XII-CBSE-Chemistry Chemical Kinetics
CBSE NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4
Back of Chapter Questions
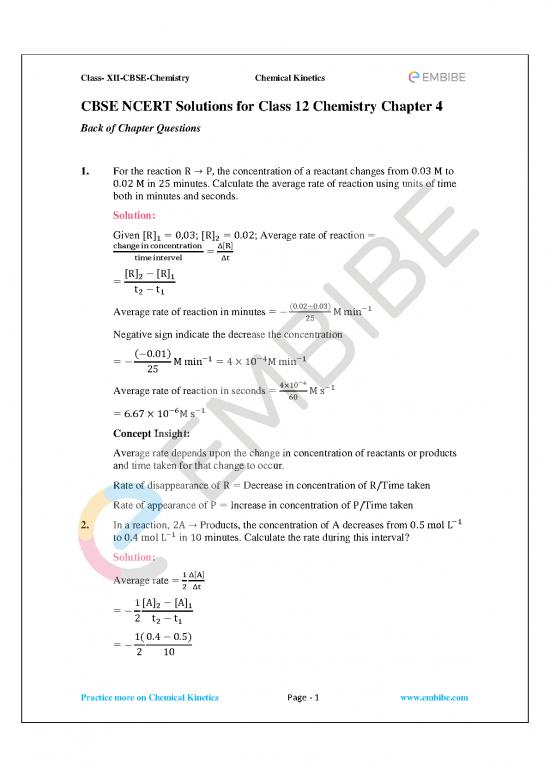
1. For the reaction R → P, the concentration of a reactant changes from 0.03 M to
0.02 M in 25 minutes. Calculate the average rate of reaction using units of time
both in minutes and seconds.
Solution:
[ ] [ ]
Given R 1 = 0,03; R 2 = 0.02; Average rate of reaction =
change in concentration Δ[R]
=
time intervel Δt
[ ] [ ]
R 2 − R 1
=
t2 −t1
Average rate of reaction in minutes = −(0.02−0.03)M min−1
25
Negative sign indicate the decrease the concentration
( )
−0.01
−1 −4 −1
=− M min =4×10 M min
25
4×10−4
Average rate of reaction in seconds = M s−1
60
−6 −1
=6.67×10 M s
Concept Insight:
Average rate depends upon the change in concentration of reactants or products
and time taken for that change to occur.
Rate of disappearance of R = Decrease in concentration of R/Time taken
Rate of appearance of P = Increase in concentration of P/Time taken
−1
2. In a reaction, 2A → Products, the concentration of A decreases from 0.5 mol L
−1
to 0.4 mol L in 10 minutes. Calculate the rate during this interval?
Solution:
[ ]
Average rate = 1Δ A
2 Δt
[ ] [ ]
1 A 2 − A 1
=−
2 t2−t1
1(0.4−0.5)
=−
2 10
Practice more on Chemical Kinetics Page - 1 www.embibe.com
Class- XII-CBSE-Chemistry Chemical Kinetics
( )
=−1 −0.1
2 10
−1 −1
=0.005 mol L min
=5×10−3M min−1
Concept Insight:
For expression the rate of reaction where stoichiometric coefficients of reactants
or products are not equal to one, rate of disappearance of any of the reactants or
rate of appearance of products is divided by their respective stoichiometric
coefficients.
1
2 2
[ ] [ ]
3. For a reaction, A + B → Product; the rate law is given by, r = k A B . What is
the order of the reaction?
Solution:
Sum of power of the concentration of the reactants in the rate law expression is
called the order of that chemical reaction.
1
2 2
[ ] [ ]
Given r = k A B .
Hence the order of the reaction = 1 + 2 = 21 = 2.5
2 2
Concept Insight: Sum of power of the concentration of the actants in the rate law
expression is called the order of the chemical reaction.
4. The conversion of molecules X to Y follows second order kinetics. If
concentration of X is increased to three times how will it affect the rate of
formation of Y?
Solution:
The reaction X → Y follows second order kinetics.
Therefore, the rate equation for this reaction will be:
2
[ ]
Rate = k X
[ ] −1
Let X = a mol L ,
then equation (1) can be written as:
Rate = k.(a)2
1
=ka2
[ ] −1
If the concentration of X is increased to three times, then X = 3a mol L
Now, the rate equation will be:
( )2 ( 2)
Rate2 = k 3a =9 ka
Practice more on Chemical Kinetics Page - 2 www.embibe.com
Class- XII-CBSE-Chemistry Chemical Kinetics
Rate =9 Rate
2 1
Hence, the rate of formation will increase by nine times.
5. A first-order reaction has a rate constant 1.15 10−3s−1. How long will 5 g of this
reactant take to reduce to 3 g?
Solution:
Given:
[ ]
Initial amount R 0 = 5 g
Final concentration [R] = 3 g
Rate constant (k) = 1.15 × 10−3s−1
Formula:
[ ]
t = 2.303log R 0
[ ]
k R
[ ] [ ]
Put the values of R 0, R , Rate constant (k) in above formula
t = 2.303 log5 second
−3
1.15×10 3
= 2.303 ×0.2219 seconds
−3
1.15×10
=444.196 second
=444 seconds (approx)
6. Time required to decompose SO Cl to half of its initial amount is 60 minutes. If
2 2
the decomposition is a first order reaction, calculate the rate constant of the
reaction.
Solution:
Given: Time required to decompose SO Cl to half of its initial amount (t ⁄ ) =
60 minutes 2 2 1 2
st
Formula for t ⁄ of 1 order reaction,
1 2
0.693
t ⁄ =
1 2
k
∴k=0.693
t ⁄
1 2
0.693
By putting the value t ⁄ in the equation the k =
1 2 60
k = 0.01155 min−1
Practice more on Chemical Kinetics Page - 3 www.embibe.com
Class- XII-CBSE-Chemistry Chemical Kinetics
k = 0.01155/60 sec−1 = 1.925×10−4s−1
7. What will be the effect of temperature on rate constant?
Solution:
The rate constant of reaction is doubled or triple with an 10 oC or K rise in
temperature.
However, the exact d rate of a chemical reaction on temperature is given by
Arrhenius equation,
Ea
−
k = Ae RT
Where,
k = rate constant
A= Arrhenius factor or the frequency factor
T= temperature
R= gas constant
Ea = activation energy
Concept Insight: The effect of temperature on rate constant is given by Arrhenius
equation.
8. The rate of the chemical reaction doubles for an increase of 10 K in absolute
temperature from 298 K. Calculate Ea.
Solution:
Given that
initial temperature (T ) = 298 K
1
( ) ( )
final temperature T = 298+10 K=308 K
2
We know that the rate of the reaction doubles when temperature is increased by
o
10 .
Therefore, let assume value of k1 = k and that of k2 = 2k
−1 −1
Also, R = 8.314 J K mol
k E T −T
Formula: ln 2 = [ 2 1]
k R T T
1 1 2
k E T −T
log 2 = [ 2 1]
k 2.303R T T
1 1 2
log2k = E [308−298]
k 2.303R 298×308
Practice more on Chemical Kinetics Page - 4 www.embibe.com
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.