188x Filetype PDF File size 0.14 MB Source: www.rba.gov.au
rba.gov.au/education
twitter.com/RBAInfo
facebook.com/
Illustrator ReserveBankAU/
youtube.com
Circular Flow Model /user/RBAinfo
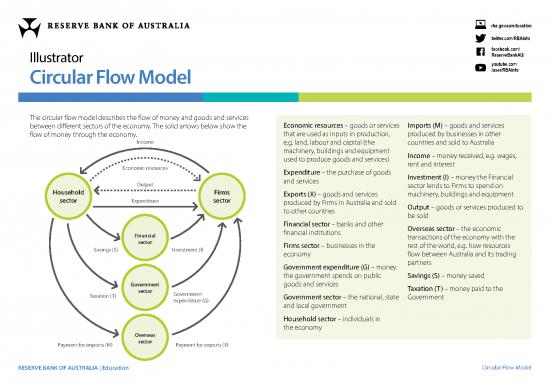
The circular flow model describes the flow of money and goods and services
between different sectors of the economy. The solid arrows below show the Economic resources – goods or services Imports (M) – goods and services
flow of money through the economy. that are used as inputs in production, produced by businesses in other
Income e.g. land, labour and capital (the countries and sold to Australia
machinery, buildings and equipment Income – money received, e.g. wages,
used to produce goods and services) rent and interest
Economic resources Expenditure – the purchase of goods
and services Investment (I) – money the Financial
Output sector lends to Firms to spend on
Household Firms Exports (X) – goods and services machinery, buildings and equipment
sector Expenditure sector produced by Firms in Australia and sold
to other countries Output – goods or services produced to
be sold
Financial sector – banks and other Overseas sector – the economic
Financial financial institutions transactions of the economy with the
sector Firms sector – businesses in the rest of the world, e.g. how resources
Savings (S) Investment (I) economy flow between Australia and its trading
Government expenditure (G) – money partners
the government spends on public Savings (S) – money saved
Government goods and services Taxation (T) – money paid to the
Taxation (T) sector Government
expenditure (G) Government sector – the national, state Government
and local government
Household sector – individuals in
the economy
Overseas
Payment for imports (M) sector Payment for exports (X)
RESERVE BANK OF AUSTRALIA | Education Circular Flow Model
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.