218x Filetype PDF File size 0.03 MB Source: www.economics.li
Questions Microeconomics (with answers)
7 Labour market
01 Demand for labour
The demand for labour is a derived demand. Explain.
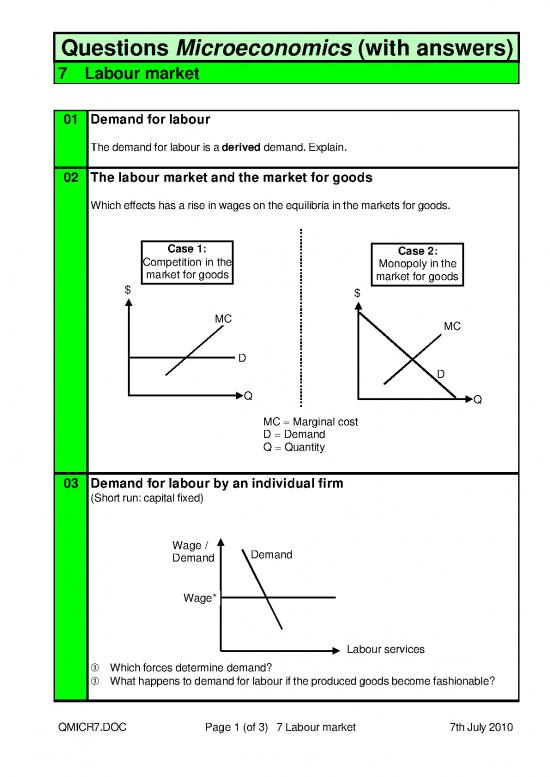
02 The labour market and the market for goods
Which effects has a rise in wages on the equilibria in the markets for goods.
Case 1: Case 2:
Competition in the Monopoly in the
market for goods market for goods
$ $
MC MC
D
D
Q Q
MC = Marginal cost
D = Demand
Q = Quantity
03 Demand for labour by an individual firm
(Short run: capital fixed)
Wage / Demand
Demand
Wage*
Labour services
À Which forces determine demand?
À What happens to demand for labour if the produced goods become fashionable?
QMICR7.DOC Page 1 (of 3) 7 Labour market 7th July 2010
04 The supply of labour by an individual worker
Wage Supply
Labour services
Explain the backward bending supply curve.
05 Minimum wage 1
Wage Supply
Demand
Labour services
Which effects has a minimum wage?
06 Minimum wage 2 (Employer is a monopsist.)
Marginal
Wage factor cost
(Labour)
Supply
Demand
Labour services
Illustrate why in this case a minimum wage can even raise labour demand.
QMICR7.DOC Page 2 (of 3) 7 Labour market 7th July 2010
07 Work or leisure time?
Case 1: Case 2:
Low (work) income High (work) income
Income Income
IC 1
IC 1
IC 2
b
IC 2
a
24 hours 24 hours
Work Work
Leisure time Leisure time
IC = Indifference curve
a + b = non-work income
b = fixe cost if working
→ Answers. Click here!
QMICR7.DOC Page 3 (of 3) 7 Labour market 7th July 2010
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.