163x Filetype PDF File size 0.09 MB Source: avys.omu.edu.tr
E&CE 261: Power Systems
STEPS TO SOLVE POWER FLOW ANALYSIS: FOR DUMMIES
1. Represent the system by its one line diagram
The point of this is to just identify all the buses in the system and see how all the
impedances relate between them. Label all the buses and write all the data that
has been given. Normally, this diagram is already given.
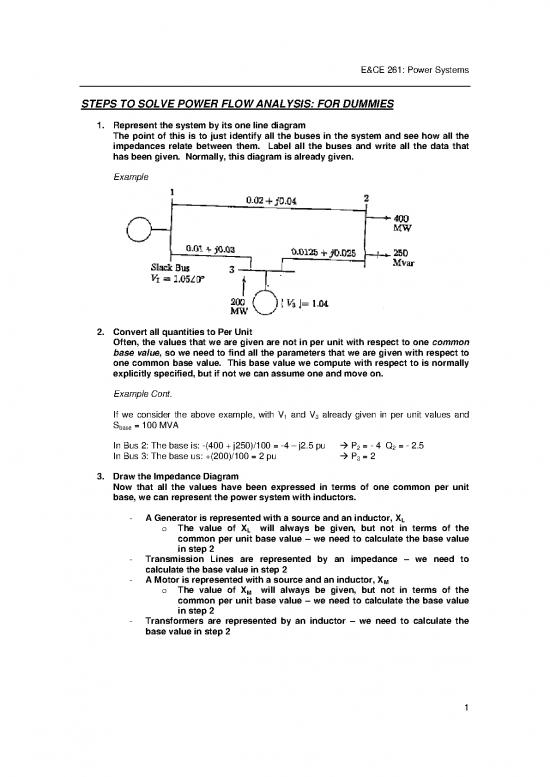
Example
2. Convert all quantities to Per Unit
Often, the values that we are given are not in per unit with respect to one common
base value, so we need to find all the parameters that we are given with respect to
one common base value. This base value we compute with respect to is normally
explicitly specified, but if not we can assume one and move on.
Example Cont.
If we consider the above example, with V and V already given in per unit values and
S = 100 MVA 1 3
base
In Bus 2: The base is: -(400 + j250)/100 = -4 – j2.5 pu P = - 4 Q = - 2.5
2 2
In Bus 3: The base us: +(200)/100 = 2 pu P = 2
3
3. Draw the Impedance Diagram
Now that all the values have been expressed in terms of one common per unit
base, we can represent the power system with inductors.
- A Generator is represented with a source and an inductor, X
L
o The value of X will always be given, but not in terms of the
L
common per unit base value – we need to calculate the base value
in step 2
- Transmission Lines are represented by an impedance – we need to
calculate the base value in step 2
- A Motor is represented with a source and an inductor, XM
o The value of X will always be given, but not in terms of the
M
common per unit base value – we need to calculate the base value
in step 2
- Transformers are represented by an inductor – we need to calculate the
base value in step 2
1
E&CE 261: Power Systems
Example Cont.
In the example above we are not given enough data to find this step (We don’t know the
voltage power, rated voltage, and inductance/impdedance)
4. Obtain the Y matrix.
bus
We now need to find the relationships between all the bus lines. We need to
calculate the self admittance and mutual admittance. For mutual admittance we
multiply by negative 1.
Example Cont.
-1 -1
Y = (0.02 + j0.04) + (0.01 + j0.03) = 20 –j50
11 -1
Y = Y = - [0.02 + j0.04] = -10 + j20
12 21 -1
Y = Y = - [0.01 + j0.03] = -10 + 30j
13 31 -1 -1
Y = (0.02 + j0.04) + (0.0125 + j0.025) = 26 – j52
22 -1
Y = Y = - [0.0125 + j0.025] = -16 + j32
23 32 -1 -1
Y = (0.01 + j0.03) + (0.0125 + j0.025) = 26 - j62
33
Note:
Y = - [Y + Y ]
11 12 13
Y = - [Y + Y ]
22 12 23
Y = - [Y + Y ]
33 23 13
Putting this all together we get:
IMPORTANT STEP: It is very useful to covert these values to polar form (|V |, θθ ):
θθ
ij ij
Note: Angles are in radians for this example, but for consistency use degrees.
5. Classify the buses as follows:
(Delta is the voltage angle)
Bus Type Given Parameters Unknown Parameters
Slack Bus V, δδ P, Q
δδ
Generator Bus P, |V| Q, δδ
δδ
Load Bus P, Q V, δδ
δδ
2
E&CE 261: Power Systems
6. Start answering the missing variables, by assumptions (unless it is specified
otherwise):
a. Slack, assume nothing
b. Generator, assume δδ = 0
δδ
c. Load, assume V = 1 pu, δδ = 0
δδ
Example Cont.
Given Required to
Bus Number Type Given Unknown Parameters Approximate
to Use
1 Slack P , Q -
V , δ 1 1 V , δ
1 1 1 1
2 Load P, Q |V |, δ P , Q |V |, δ
2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
3 Voltage P, |V| Q, δ P , |V | δ
3 3 3 3 3 3 3
Assume (for now) that:
|V | = 1 pu
2
δ = 0
2
δ = 0
3
7. Find approximations for the Real and Reactive Power that we are given, using the
assumed and given values for voltage/angles/admittance. Find the difference in
this with the value that was actually given.
Example Cont.
We now need equations for P , Q , and P :
2 2 3
We know all these parameters so we can solve for the first approximation of P P and
Q 2, 3,
2
We find:
P = -1.14
2
P = 0.5616
3
Q2 = -2.28
Since we know P , Q , and P , we can find ∆P , ∆Q , and ∆P :
2 2 3 2 2 3
3
E&CE 261: Power Systems
∆value = Given Value – Approximated Value
8. Write the Jacobian Matrix for the first iteration of the Newton Raphson Method.
This is in the form:
[∆∆values] = [Jacobian Matrix] * [∆∆ for Unknown Parameters]
∆∆ ∆∆
Example Cont.
So in this case we know ∆P , ∆Q , and ∆P and need to find the Jacobian partial
2 2 3
derivatives for the unknown values: δ , δ , |V |,
2 3 2
So this means the Jacobian matrix is a 3x3 matrix, so we need to find 9 partial
derivatives.
We can do this as follows:
4
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.